Handling Hallucinations in Alzheimer’s Dementia
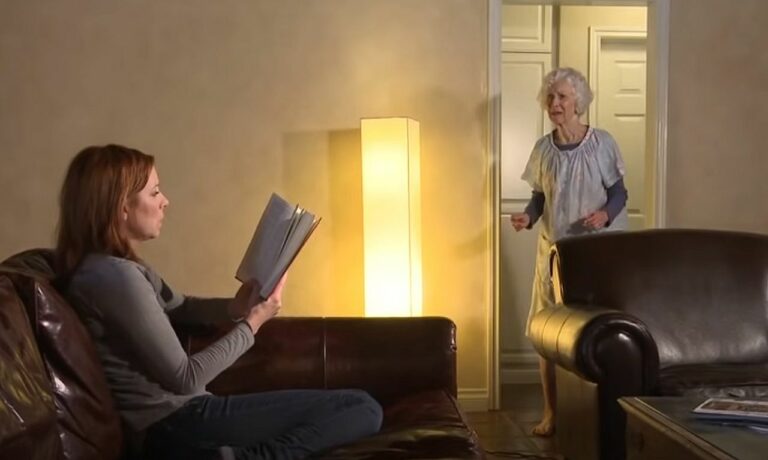
A person with dementia can experience hallucinations when the regions of the brain responsible for interpreting sights and sounds are affected. Here are ways to deal with it.

A person with dementia can experience hallucinations when the regions of the brain responsible for interpreting sights and sounds are affected. Here are ways to deal with it.

A diet that combines unsaturated fats with nitrite-rich vegetables, such as olive oil and lettuce, can protect you from hypertension and vascular dementia.

Most of the time, it takes a combination of genetics, bad environment and unhealthy lifestyle to trigger Alzheimer’s. However, one gene called apolipoprotein E (APOE) can make a big difference.

A new study suggests that very low sodium intake may be linked to faster memory decline in older adults.

A diet that combines unsaturated fats with nitrite-rich vegetables, such as olive oil and lettuce, can protect you from hypertension and vascular dementia.

Most of the time, it takes a combination of genetics, bad environment and unhealthy lifestyle to trigger Alzheimer’s. However, one gene called apolipoprotein E (APOE) can make a big difference.

In a study on health & cynicism, people were asked how much they agree with statements such as, “I think most people would lie to get ahead,” and “It is safer to trust nobody”. The clear connection between their answers and their risk of dementia may startle you.

Lewis Hornby had a problem: his grandmother with dementia wasn’t drinking enough, causing her to get severely dehydrated.
No spam, only news and updates.