Lymphatic systems serve many tasks, including the draining of waste proteins. A unexpected new discovery found it reaches brain cells. Can it be boosted to drain Alzheimer’s dangerous plaques?
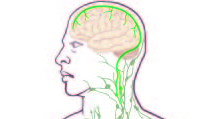
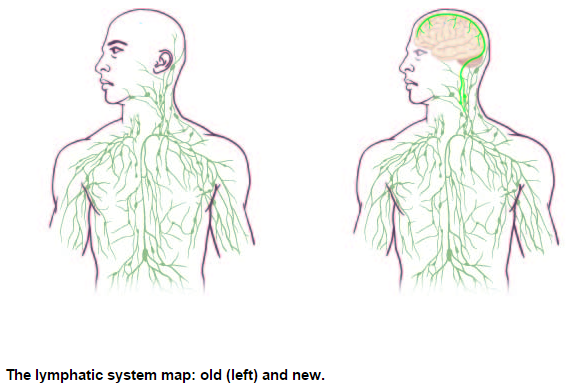
In a stunning discovery that overturns decades of textbook teaching, researchers at the University of Virginia School of Medicine have determined that the brain is directly connected to the immune system by vessels previously thought not to exist.
That such vessels could have escaped detection when the lymphatic system has been so thoroughly mapped throughout the body is surprising on its own, but the true significance of the discovery lies in the effects it could have on the study and treatment of neurological diseases ranging from autism to Alzheimer’s disease to multiple sclerosis.
“Instead of asking, ‘How do we study the immune response of the brain?,’ ‘Why do multiple sclerosis patients have the immune attacks?,’ now we can approach this mechanistically – because the brain is like every other tissue connected to the peripheral immune system through meningeal lymphatic vessels,” said Jonathan Kipnis, a professor in U.Va.’s Department of Neuroscience and director of U.Va.’s Center for Brain Immunology and Glia. “It changes entirely the way we perceive the neuro-immune interaction. We always perceived it before as something esoteric that can’t be studied. But now we can ask mechanistic questions.”
He added, “We believe that for every neurological disease that has an immune component to it, these vessels may play a major role. [It’s] hard to imagine that these vessels would not be involved in a [neurological] disease with an immune component.”
Kevin Lee, who chairs the Department of Neuroscience, described his reaction to the discovery by Kipnis’ lab: “The first time these guys showed me the basic result, I just said one sentence: ‘They’ll have to change the textbooks.’ There has never been a lymphatic system for the central nervous system, and it was very clear from that first singular observation – and they’ve done many studies since then to bolster the finding – that it will fundamentally change the way people look at the central nervous system’s relationship with the immune system.”
Even Kipnis was skeptical initially. “I really did not believe there are structures in the body that we are not aware of. I thought the body was mapped,” he said. “I thought that these discoveries ended somewhere around the middle of the last century. But apparently they have not.”
The discovery was made possible by the work of Antoine Louveau, a postdoctoral fellow in Kipnis’ lab. The vessels were detected after Louveau developed a method to mount a mouse’s meninges – the membranes covering the brain – on a single slide so that they could be examined as a whole. “It was fairly easy, actually,” he said. “There was one trick: We fixed the meninges within the skullcap, so that the tissue is secured in its physiological condition, and then we dissected it. If we had done it the other way around, it wouldn’t have worked.”
After noticing vessel-like patterns in the distribution of immune cells on his slides, he tested for lymphatic vessels and there they were. The impossible existed.
The soft-spoken Louveau recalled the moment: “I called Jony [Kipnis] to the microscope and I said, ‘I think we have something.’”
As to how the brain’s lymphatic vessels managed to escape notice all this time, Kipnis described them as “very well hidden” and noted that they follow a major blood vessel down into the sinuses, an area difficult to image. “It’s so close to the blood vessel, you just miss it,” he said. “If you don’t know what you’re after, you just miss it.
“Live imaging of these vessels was crucial to demonstrate their function, and it would not be possible without collaboration with Tajie Harris,” Kipnis noted. Harris is an assistant professor of neuroscience and a member of the Center for Brain Immunology and Glia. Kipnis also saluted the “phenomenal” surgical skills of Igor Smirnov, a research associate in the Kipnis lab whose work was critical to the imaging success of the study.
The unexpected presence of the lymphatic vessels raises a tremendous number of questions that now need answers, both about the workings of the brain and the diseases that plague it.
For example, take Alzheimer’s disease. “In Alzheimer’s, there are accumulations of big protein chunks in the brain,” Kipnis said. “We think they may be accumulating in the brain because they’re not being efficiently removed by these vessels.” He noted that the vessels look different with age, so the role they play in aging is another avenue to explore.
And there’s an enormous array of other neurological diseases, from autism to multiple sclerosis, that must be reconsidered in light of the presence of something science insisted did not exist.
The findings have been published online by the prestigious journal Nature and will appear in a forthcoming print edition. The article’s authors are Louveau, Smirnov, Timothy J. Keyes, Jacob D. Eccles, Sherin J. Rouhani, J. David Peske, Noel C. Derecki, David Castle, James W. Mandell, Lee, Harris and Kipnis.
The study was funded by National Institutes of Health grants R01AG034113 and R01NS061973. Louveau was a fellow of Fondation pour la Recherche Medicale.
SOURCE:
Josh Barney, U.Va. Health System



Physicians knows that the Lymphatic System reacts as a "Whole Body and Integrated System" to fight against infections ,in any part of the body ,as for example ,Urinary Tract Infections ,and others types of infections (including acute and chronic teeth and gums infections, etc) and gut leaks of toxins.
As is well known too , different research articles published in the lasts ten years , proved that by the so called "Gut Brain Axis" , the gut can leaks toxins from it " bad" bacterias , to the brain , causing brain disorders as anxiety , depression , fybromyalgia , neuroinflammation , etc.
Maybe one of the main "ways" of the so callled Gut Brain Axis leaking of toxins , is by it lymphatic system of the brain ,leading to proliferation and reaction of microglia (the macrophages of the brain) to fight against toxins .Researchers are concluding that if someone do Not keeps a heathy gut flora, the "bad" bacterias of the gut ,can predominate, and it "bad" bacterias leaks toxins to the brain ,probably just by the lymphatic system that links to inside the brain.
Then to keeps a healthy gut flora , keeping Good bacterias in the gut , taking daily PRObiotics (as yogurts and/or supplements with the Good bacterias lactobacillus acidophilus and bifidobacterium, etc. ) and to takes PREbiotics as oat bran , that synergistically can protects the gut against the "bad" bacterias.
Elderly patients with or without dementias, could do check ups to looks for sources of acute or chronic infections in different parts of theirs bodies , to treat it, and could takes daily , supplements with probiotics, to helps to "calm down" the lymphatic system of the brain .
Maybe that's why ultrasound of the brain removes plaques from the brains of lab rodents. Perhaps the mechanical stimulation increases lymph drainage so the amyloid plaques can be removed.
You really need to do a better job of crediting your source. This is very close to plagerism – reprinted in this way without express permission by the author it is plagerism.
You really need to hold your horses. The sources for every article on this site appear at the end of each article. This article is sourced from the University of Virginia's official press release, which does not only qualify as permission, but as an endorsement, as well.