Gene Therapy Slows Huntington’s Progression 75% — Including Dementia
For the first time, a one-time treatment has shown the ability to slow Huntington’s decline — including dementia symptoms — over three years.

For the first time, a one-time treatment has shown the ability to slow Huntington’s decline — including dementia symptoms — over three years.

The first 3D-printed brain tissue that can grow and function like typical brain tissue is a major breakthrough for scientists in search of an Alzheimer’s cure.

Research shows that a blood test now on the market accurately identifies brain amyloid status with a single blood sample. In other words, this blood test can diagnose Alzheimer’s.

A massive study of medical and genetic data shows that people with a particular version of a gene involved in immune response had a lower risk of Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s disease.

Scientists at Oregon’s only public academic health center (OHSU) have discovered a new avenue of cell death in Alzheimer’s disease and vascular dementia.
Tau PET is an imaging test used to detect the presence of tau protein in the brain. Researchers say it’s the best way to predict the rate of cognitive decline due to Alzheimer’s.

Dr. Robert Przybelski has prescribed lecanemab to real-life patients, and discusses his experience prescribing and administering the treatment.

Now, a third new Alzheimer’s drug expected to be approved by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA),. The field of new drugs is beginning to show progress in the fight to slow the disease.

The FDA has approved generic lecanemab (brand name Leqembi®). The new drug can slow the progression of Alzheimer’s. Two top doctors discuss the pros and cons.
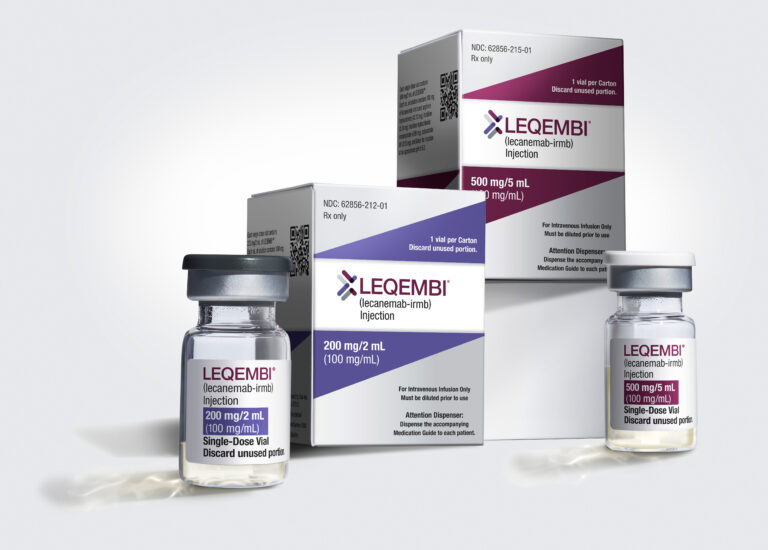
The FDA Advisory Committee’s endorsement of Leqembi paves way for traditional approval, ushers in a new era for Alzheimer’s

Researchers find optimistic people contribute to the health of their partners, staving off risk factors leading to Alzheimer’s disease, other dementias and cognitive decline as they grow old together.

Bringing art and creativity into elder care settings helps families reconnect with loved ones who have dementia. In this moving talk, Anne Bastings shares how.

When a hurricane hits Florida — or anywhere that has a very large population of people with dementia, there are special preparations that should be made by those living with dementia. Check these dementia-in-a-storm readiness lists.

Researchers find optimistic people contribute to the health of their partners, staving off risk factors leading to Alzheimer’s disease, other dementias and cognitive decline as they grow old together.

Bringing art and creativity into elder care settings helps families reconnect with loved ones who have dementia. In this moving talk, Anne Bastings shares how.

When a hurricane hits Florida — or anywhere that has a very large population of people with dementia, there are special preparations that should be made by those living with dementia. Check these dementia-in-a-storm readiness lists.

In gardening, people with Alzheimer’s grow fresh plants along with better thinking. It’s a pleasant way to make things easier.
No spam, only news and updates.