(Toronto, ON.) – Approximately 500 billion cups of coffee are consumed worldwide each year.
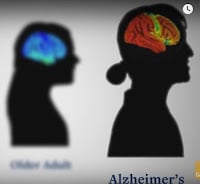
A new study out of the Krembil Brain Institute, part of the Krembil Research Institute, suggests there could be more to that morning jolt of goodness than a boost in energy and attention. Drinking coffee may also protect you against developing both Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s disease.
Decreased Alzheimer’s Risk – But Why?
“Coffee consumption does seem to have some correlation to a decreased risk of developing Alzheimer’s disease and Parkinson’s disease,” says Dr. Donald Weaver, Co-director of the Krembil Brain Institute. “But we wanted to investigate why that is – which compounds are involved and how they may impact age-related cognitive decline.” (Article continued below video…)
Dr. Weaver enlisted Dr. Ross Mancini, a research fellow in medicinal chemistry and Yanfei Wang, a biologist, to help. The team chose to investigate three different types of coffee – light roast, dark roast, and decaffeinated dark roast.
3 Roast Coffees – Unexpected Results
“The caffeinated and de-caffeinated dark roast both had identical potencies in our initial experimental tests,” says Dr. Mancini. “So we observed early on that its protective effect could not be due to caffeine.”
Dr. Mancini then identified a group of compounds known as phenylindanes, which emerge as a result of the roasting process for coffee beans. Phenylindanes are unique in that they are the only compound investigated in the study that prevent – or rather, inhibit – both beta amyloid and tau, two protein fragments common in Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s, from clumping. “So phenylindanes are a dual-inhibitor. Very interesting, we were not expecting that.” says Dr. Weaver.
Dark Roast More Protective
As roasting leads to higher quantities of phenylindanes, dark roasted coffee appears to be more protective than light roasted coffee.
“It’s the first time anybody’s investigated how phenylindanes interact with the proteins that are responsible for Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s,” says Dr. Mancini. “The next step would be to investigate how beneficial these compounds are, and whether they have the ability to enter the bloodstream, or cross the blood-brain barrier.”
Natural Compound
The fact that it’s a natural compound versus synthetic is also a major advantage, says Dr. Weaver.
“Mother Nature is a much better chemist than we are and Mother Nature is able to make these compounds. If you have a complicated compound, it’s nicer to grow it in a crop, harvest the crop, grind the crop out and extract it than try to make it.”
But, he admits, there is much more research needed before it can translate into potential therapeutic options.
“What this study does is take the epidemiological evidence and try to refine it and to demonstrate that there are indeed components within coffee that are beneficial to warding off cognitive decline. It’s interesting but are we suggesting that coffee is a cure? Absolutely not.”
- Ross S. Mancini, Yanfei Wang, Donald F. Weaver. Phenylindanes in Brewed Coffee Inhibit Amyloid-Beta and Tau Aggregation. Frontiers in Neuroscience, 2018; 12 DOI: 10.3389/fnins.2018.00735
SOURCES:
-
Krembil Research Institute
The Krembil Research Institute (or “Krembil”) is one of the principal research institutes of the University Health Network. The Krembil is focused on research programs dedicated to brain & spine, arthritis and vision disorders with a goal to alleviate debilitating chronic disease through basic, translational and clinical research. Krembil is located at the Toronto Western Hospital in downtown Toronto. -
University Health Network
University Health Network consists of Toronto General and Toronto Western Hospitals, the Princess Margaret Cancer Centre, Toronto Rehabilitation Institute, and The Michener Institute of Education at UHN. The scope of research and complexity of cases at University Health Network has made it a national and international source for discovery, education and patient care. It has the largest hospital-based research program in Canada, with major research in cardiology, transplantation, neurosciences, oncology, surgical innovation, infectious diseases, genomic medicine and rehabilitation medicine. University Health Network is a research hospital affiliated with the University of Toronto.